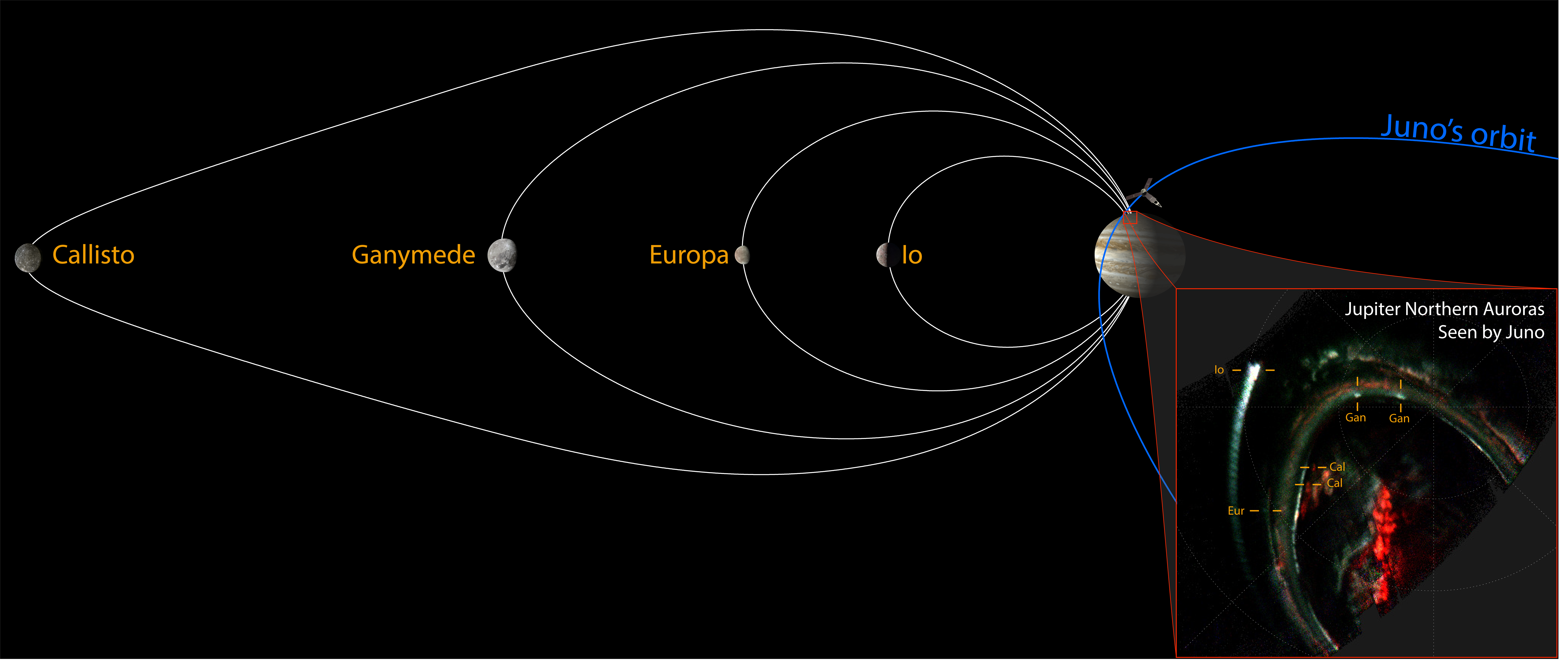
Jupiter has the most intense auroras in the Solar System. Some of these are linked to electromagnetic interactions between the planet and its four Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These particular emissions, called “auroral fingerprints,” are distinguishable in several spectral ranges, including ultraviolet, infrared, and radio. They result from charged particles circulating along the magnetic field lines connecting each moon to Jupiter, producing specific auroras in the atmosphere of the gas giant. Until now, only the signatures of three moons had been clearly identified by the Hubble Space Telescope in the early 2000s.
Since July 2016, the Juno probe has been repeatedly flying over Jupiter’s auroral regions and providing unique diagnostics thanks to its onboard instruments. The UVS spectrograph, in particular, allows for detailed monitoring of the evolution of auroral signatures as a function of local conditions and the properties of the solar wind, which modulates the extent of Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Despite these unprecedented measurements, no clear detection of Callisto’s signature had yet been reported, as its expected brightness is low and its position is very close to Jupiter’s powerful main emissions.
However, a team of French researchers (IRAP, LAM, LIRA, ISAE-Supaero, LATMOS) participating in NASA’s Juno mission has just provided observational evidence of this imprint in a study published in Nature Communications. They showed that in September 2019, an exceptional shift in Jupiter’s main auroral emissions, caused by a global expansion of the magnetosphere in response to particular solar wind conditions, revealed Callisto’s ultraviolet signature. For the first time, the auroral signatures of the four Galilean moons were observed simultaneously at the planet’s north pole.
Joint analysis of UVS emissions and particle and wave measurements recorded by Juno shows that the signatures of the four moons are based on common physical mechanisms. This discovery completes the picture of the couplings between Jupiter and its satellites and opens up new perspectives for the study of magnetospheric interactions around giant planets.
Link to the NASA press release: https://science.nasa.gov/missions/juno/juno-detected-the-final-missing-auroral-signature-from-jupiters-four-largest-moons/
Link to the INSU press release: https://www.insu.cnrs.fr/fr/cnrsinfo/juno-identifie-lempreinte-aurorale-manquante-de-la-lune-callisto-sur-les-poles-de-jupiter
.




